The mircogrid can operate in both island mode or grid-connected mode:
According to the different size, technical sophistication, application/solution and geographic location, microgrids can take a varity of forms and structures from residential. There are five commonly used classes of microgrids:
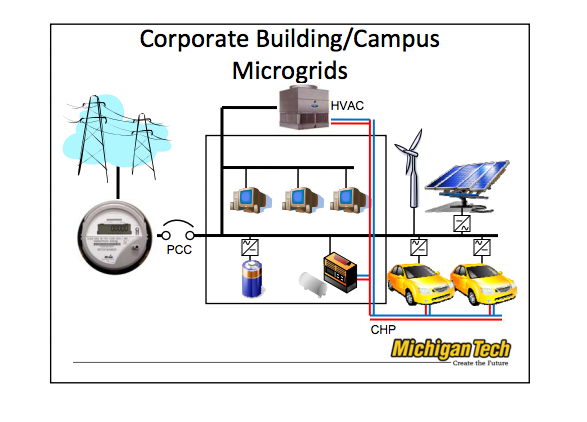
1.Campus Environment/ institutional microgrids
The focus of campus Microgrids is aggregating existing on-site generation with multiple
loads that are co-located in a campus or institutional setting (e.g., industrial park).
2.Remote ''Off-grid'' microgrids
An "off-grid" microgrid is usually built in areas that are far distant from any tras-mission and distribution infrastructure and, therefore, have no connection to the utility grid. Due to this, such a microgrid must have black start capability.
3.Military Base Microgrid
These Microgrids are being actively deployed with focus on both physical and cyber security for military facilities in order to assure reliable power without relying on the Macrogrid.
4.Commercial and industrial microgrids
Main reasons for the installation of an industrial microgrid are power supply security and its reliability. There are many manufacturing processes in which an interruption of teh power supply may cause high revenue losses and long start-up time.
5.Community/utility microgrids
A utility microgrid may include a distribution feeder, a complete medium voltage distribution substation or even several distribution substations in a large area.
In order to design the most suitable microgrid system for different cases, more further study need to be done.
Information is available from:
https://www.google.co.uk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0CCAQFjAA&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.siemens.com%2Fdownload%3FDLA17_8&ei=bQ3ZVNv_IpXsaM_DgOgH&usg=AFQjCNGmsCSC4H6ErwvvwbbxGKrr2sJWyg&sig2=504NDRHfP_NmqgQZZvs2yg
https://www.securicon.com/sites/default/files/Introduction%20to%20Microgrids%20-%20Securicon%20-%202013_1.pdf
http://www.slideshare.net/jucovas/ssd-final-webpage-31204569?related=10
https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/us/Documents/energy-resources/us-er-2014-aes-presentation-es7-topic6-112614.pdf












没有评论:
发表评论